Scientists consider the future of ‘biocomputers’

As synthetic intelligence computer software and sophisticated desktops revolutionize contemporary know-how, some scientists see a potential wherever laptop or computer programmers leap from silicon to organic and natural molecules.

Experts with Johns Hopkins University are investigating the probability of “biocomputers” – plans modelled from natural and organic molecules these kinds of as human DNA or proteins – unlocking new insights on human biology and advancing the processing electric power of upcoming tech.

A lot of these technological anticipations derive from a little something named “organoids,” which are lab-grown tissues resembling fully developed organs, sharing related biological complexities to tissues comprised in kidneys, lungs and mind cells.

Organoids, which have develop into extra outstanding in labs more than the last two many years, at present offer you researchers a additional moral choice to animal or human screening, mimicking essential features of cells and advancing scientific understandings to how individuals cells function.

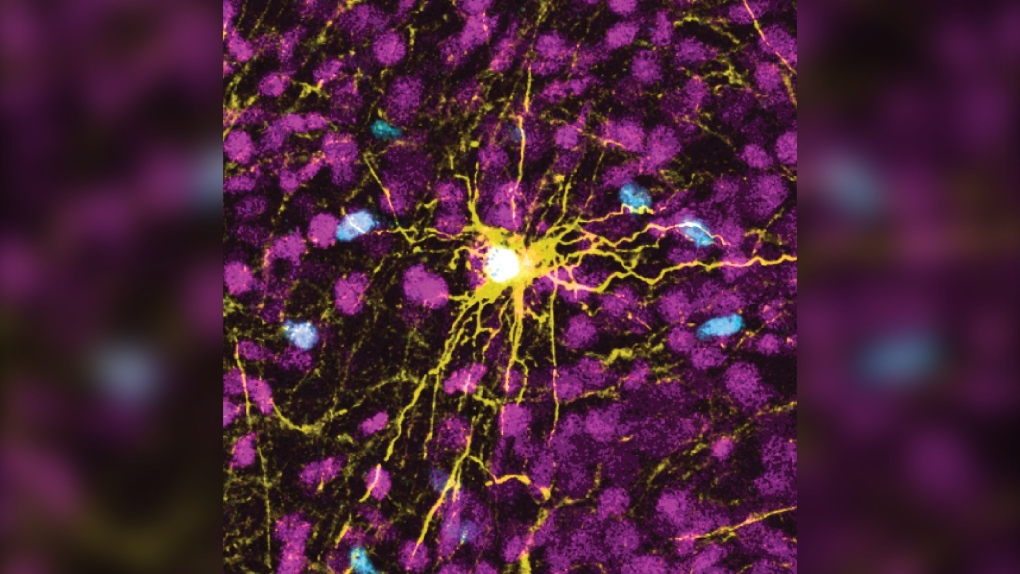
Most just lately, experts with Johns Hopkins have been examining the mother nature of “brain organoids,” which are orbs the sizing of a pen dot that mirror the primary neural functions of discovering and remembering in the human brain, in accordance to a news release.

“This opens up investigate on how the human mind works,” Thomas Hartung, a professor of environmental overall health sciences at Johns Hopkins, said in the launch, introducing that deeper insights into human cognition can also provide as a roadmap for unlocking better computing electrical power in foreseeable future technological know-how.

“Computing and synthetic intelligence have been driving the engineering revolution but they are reaching a ceiling,” he reported. “Biocomputing is an huge work of compacting computational power and raising its efficiency to drive past our present technological limitations.”

Hartung and his staff initial began increasing brain organoids in 2012 by using cells from human skin samples that they reprogrammed to multiply and mirror the functions of other cells. Each individual of these organoids consist of close to 50,000 cells, and Hartung and his workforce visualize constructing a futuristic pc that makes use of the firm of these cells as a basis for new types of computer programming.

Inspite of the simple fact that laptop calculations involving figures and knowledge are significantly top-quality to brains in conditions of pace and quantity, Hartung pointed out that human beings are at the moment additional effective in arriving at sophisticated logical selections with considerably much less processing energy needed.

For instance, our skill to tell the variation between a cat and a doggy dependent on a swift glance requires substantially considerably less processing electrical power than a computer system method would demand, even with the fact that an progress computer system would be equipped to present way much more information on each and every species than the ordinary particular person.

By way of employing the complexity of mind organoids and coaching them with synthetic intelligence, Hartung thinks “biocomputers” can attain new computing velocity, processing energy, storage abilities, and normal facts performance.

“Computers that run on this ‘biological hardware’ could in the future ten years start off to alleviate vitality use calls for of supercomputing that are getting increasingly unsustainable,” he reported.

He extra that it could be many years right before an organoid-centered computer system would proficiently functionality, but that the chance remains as the field of organoid investigate expands.

Lena Smirnova, a Johns Hopkins assistant professor of environmental wellness and engineering, who is co-major the investigation, added that these kinds of analysis could revolutionize drug testing exploration for neurodegeneration and neurodevelopmental ailments.

“The instruments we are creating towards organic computing are the very same resources that will make it possible for us to understand improvements in neuronal networks particular for autism, with out getting to use animals or to entry patients,” she stated in the information launch. By advancing bio-computing, Smirnova believes researchers can “understand the underlying mechanisms of why people have these cognition challenges and impairments.”

Smirnova and Hartung additional outlined their programs for evaluating the potential of organoid intelligence and bio-computing in the journal Frontiers in Science last month.
