
New materials for the computer of the future
Novel products could revolutionize computer technological innovation. Study carried out by scientists at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI using the Swiss Light-weight Resource SLS has arrived at an essential milestone along this route.
Microchips are designed from silicon and get the job done on the bodily principle of a semiconductor. Almost nothing has changed in this article since the initially transistor was invented in 1947 in the Bell Labs in The usa. Ever since, scientists have frequently foretold the conclusion of the silicon era—but have generally been mistaken.
Silicon technological innovation is pretty much alive, and carries on to develop at a quick speed. The IT huge IBM has just introduced the to start with microprocessor whose transistor buildings only evaluate two nanometers, equivalent to 20 adjacent atoms. So what’s future? Even tinier buildings? Presumably so—for this 10 years, at least.
At the identical time, new tips are taking shape in investigate laboratories about a innovative engineering that could transform anything we consider we know about microelectronics on its head. A person of the shining lights in this study subject is delivered by Milan Radovic’s staff. Milan Radovic functions at the Paul Scherrer Institute and his staff just printed an report in the journal Communications Physics presenting sensational findings from cutting-edge research into transparent oxides (TOs) that could open up up huge prospective buyers for this novel engineering.
Revolutionary microchips
Radovic and his co-authors Muntaser Naamneh and Eduardo Guedes, collectively with the Bharat Jalan exploration group from the College of Minnesota do not work with silicon, but with changeover steel oxides (TMOs). These exhibit exotic qualities and multifunctional phenomena such as significant-temperature superconductivity, colossal magnetoresistance, metallic-insulator changeover and substantially far more apart from. What may at first sound bewildering to a lay human being claims enormous advances for the chip know-how of the long term.
In their newest publication, the scientists aim on barium tin oxide (BaSnO3), a material that combines optical transparency with high electrical conductivity.
Researchers have been trying for some time to elicit semiconductor-like houses from transition metals as well as particular clear oxides these kinds of as BaSnO3 and strontium stannate (SrSnO3). In comparison with silicon, they offer floor-breaking advantages for optoelectronic features: these transparent, conductive perovskite oxides, would make it attainable to build switching features with right connected electrical and optical homes. It may possibly then be conceivable to produce transistors that can be switched with light.
Awareness of interfaces is significant
All microchips are created from a mixture of unique substances. To realize their operate, it is crucial to know what takes place in the skinny adjacent levels, or interfaces, in between these resources, mainly because the actual physical qualities of lots of products are totally different on the area compared with their inside.
“Unique phases” can arise at the interfaces of materials—a discovery manufactured by a few British physicists who were awarded the Nobel Prize in 2016. The write-up just revealed describes significant improvements in the comprehension of the surface area-condition electronic qualities of BaSnO3.
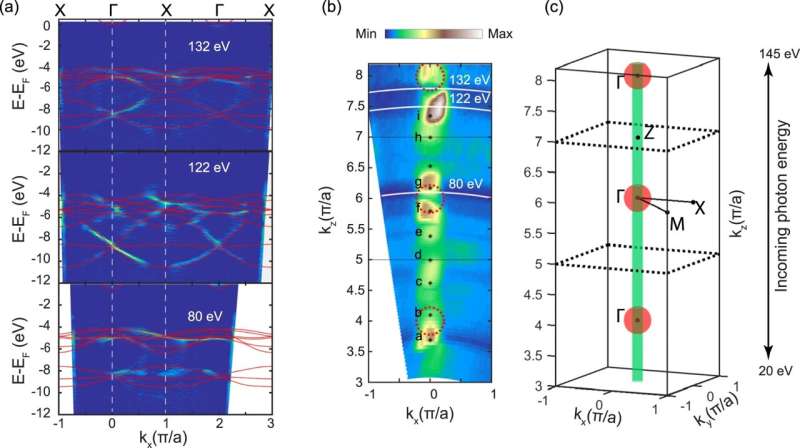
The researchers employed angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy at the beamline of the Swiss Gentle Source SLS to “find out the two-dimensional electronic state of BaSnO3 , which opens up new prospects for this class of materials,” claims Eduardo Guedes.
Now the researchers want to locate out which other supplies exhibit related homes and could be probable candidates for the optical microchips of the foreseeable future.
But silicon is far from currently being an outdated engineering, Milan Radovic states. It is in simple fact highly created and effective. “Nevertheless, know-how dependent on transition metallic oxides is substantially far more powerful and versatile—its time will occur.”
Muntaser Naamneh et al, Small-dimensional digital state at the floor of a transparent conductive oxide, Communications Physics (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s42005-022-01091-y
Citation:
New components for the pc of the upcoming (2022, December 8)
retrieved 8 December 2022
from https://techxplore.com/information/2022-12-resources-long run.html
This document is matter to copyright. Apart from any truthful dealing for the goal of personal analyze or investigation, no
component may possibly be reproduced without having the composed permission. The material is supplied for data applications only.
